Architecture
This section details the technical architecture of our RISC Zero + Cartesi integration, focusing on the interaction between components and the proof verification flow.
System Components
The integration consists of three main components that work together to generate and verify zero-knowledge proofs:
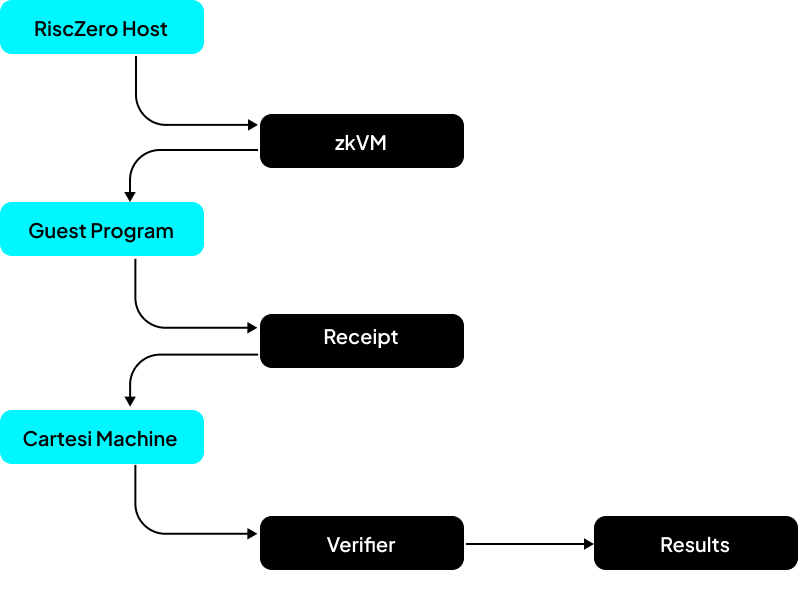
The process begins when the Host prepares private inputs and the Guest performs confidential computation, after which RISC Zero generates and serializes a cryptographic proof receipt. Finally, the Cartesi Machine deserializes the receipt, and its verifier program validates the proof.
1. RISC Zero Host Program
The host program orchestrates the proof generation process:
// Example host program structure
fn main() {
// Configure proving method (local or remote)
let prover = default_prover();
// Initialize zkVM with private inputs
let env = ExecutorEnv::builder()
.write(&private_input)
.build()
.unwrap();
// Generate proof (returns Composite(default), Succinct, or Groth16 receipt)
let receipt = prover
.prove_with_opts(env, GUEST_ELF, &ProverOpts::default())
.unwrap();
// Serialize receipt for Cartesi verification
let receipt_bytes = bincode::serialize(&receipt).unwrap();
}
Key responsibilities:
- Manages the proof generation pipeline (proof strategy, receipt type, resources)
- Prepares private inputs and serializes proof data for Cartesi verification
2. RISC Zero Guest Program
The guest program defines the computation to be proven:
use risc0_zkvm::guest::env;
fn main() {
// Read private inputs
let private_data: Vec<u8> = env::read();
// Perform confidential computation
let result = process_private_data(private_data);
// Optional: Verify computation constraints
verify_constraints(&result)?;
// Commit public outputs to journal
env::commit(&result);
}
Design considerations:
- Optimizes for efficient proving with clear I/O boundaries
- Implements selective disclosure and STARK-based proof generation
3. Cartesi Verifier
The verifier program runs inside the Cartesi Machine and validates RISC Zero proofs:
fn main() {
// Read serialized receipt from Cartesi input drive
let receipt_bytes = read_from_input_drive();
let receipt: Receipt = deserialize(&receipt_bytes)?;
// Verify cryptographic proof
match receipt.verify(RISC0_IMAGE_ID) {
Ok(journal) => {
// Process verified public outputs
handle_verified_result(journal);
emit_verification_success();
},
Err(e) => emit_verification_failure(e),
}
}
Verification capabilities:
- Validates cryptographic proofs across all RISC Zero receipt types
- Manages verification state and reports results to the rollup